Building supply reliability for lower carbon energy
Moving transport into a lower carbon future, with less environmental impact
The pressure is on to decarbonize transportation—the source of nearly a quarter of U.S. CO2 emissions. Yet the road ahead is complex. EV manufacturers face cost pressures and uncertain policy support, while marine operators must meet tightening emissions rules and long-term climate goals without disrupting global trade. That’s why we’re building innovative approaches to delivering consistently reliable low-carbon energy products and solutions with less environmental impact.
~1/4
3%
87%
~3x
Our 140-year history of supporting the transportation sector—from energy and chemicals to lubricants—helps position us to deliver lower-carbon solutions that strengthen supply chains, meet production demands, and reduce emissions, providing manufacturers and operators with reliable, energy security for the future.
Our approach
For more than 140 years, ExxonMobil has paired technical ingenuity with the ability to make innovations commercially viable. Our researchers helped pioneer lithium battery technology—a breakthrough recognized with a Nobel Prize. Today, we bring that same leadership to the transportation sector, supporting the development of a reliable, domestic lithium supply.
Forward-thinking solutions designed for the transportation industry
We’re focused on creating innovative solutions that drive value and strengthen the lithium supply chain. Our advanced approach to production processes has the potential to unlock vast domestic lithium resources, helping enhance U.S. energy security. Mobil™ Lithium is planned to deliver lower-carbon intensity lithium compared to hard rock mining5 through Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE), providing the transparency and reliability customers need to meet emissions-reduction priorities.
Moving forward with confidence
Our experts combine insight across science, finance, and policy to help EV manufacturers and battery producers navigate evolving regulations and identify opportunities for funding and project support. We are working to scale DLE to build a reliable, large-scale North American lithium supply. With global lithium demand expected to quadruple by 2030, we’re preparing to help you create long-term value and resilient growth.
Lithium pathway
Accelerating low carbon transportation with lithium solutions
Deep lithium-rich brines:
Lithium-rich brine is sourced from deep underground rock formations. Advanced reservoir engineering and drilling capabilities allow for efficient access to these advantaged resources.
Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE):
Using DLE, a method with lower carbon intensity than hard rock mining, lithium is separated from the brine and upgraded to battery-grade material onsite.
Electric vehicle (EV) batteries:
This critical material is supplied to manufacturers to meet the growing demand for high-performance EV batteries.
Passenger vehicle:
By the early 2030s, the aim is to produce enough lithium to supply the manufacturing needs of approximately 1 million EVs annually.
Lower emissions:
DLE technology provides a more reliable, lower-carbon source of lithium. This strengthens the environmental benefit of EVs by reducing the carbon intensity of the supply chain.
Our approach
Proven marine leadership
For decades, ExxonMobil has worked with the transportation sector across energy, chemicals, and lubricants, bringing a legacy of collaboration and technical execution. Our experience operating global energy systems in the marine sector supports us in delivering lower-carbon fuels that meet strict marine regulations and high-performance demands.
Pragmatic solutions
With years of experience as a trusted technical advisor and operating global energy systems, we’re pursuing low-carbon ammonia backed by advantaged natural gas and carbon capture and storage (CCS)—to helping marine operators adopt lower-carbon fuels with fewer unknowns.
Business value
As leaders in creating new markets for low carbon intensity ammonia, we are committed to engaging marine-sector partners globally to explore future offtake opportunities aligned with our developing supply.

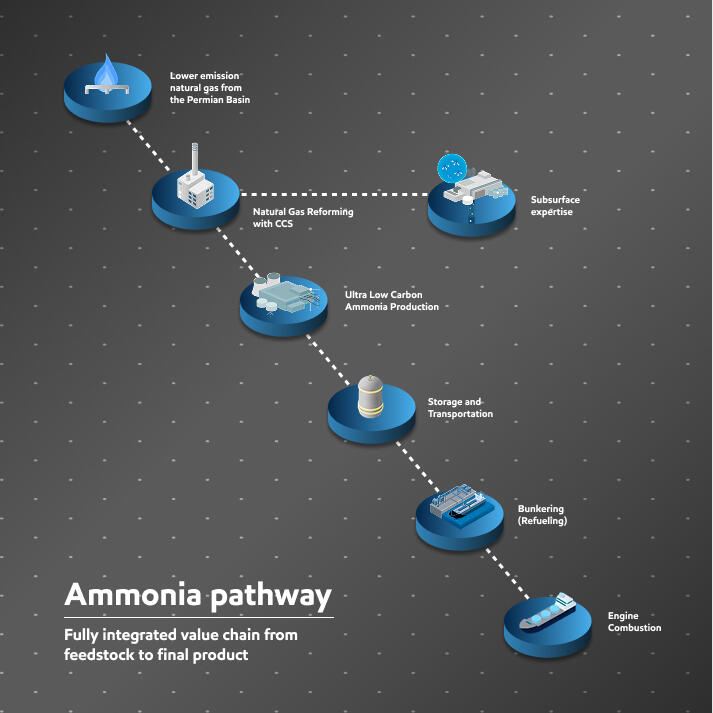
Ammonia pathway
Unlocking tomorrow’s low-carbon transportation with ammonia-powered solutions
Feedstock sourcing:
Hydrogen is produced using lower-emission natural gas from the Permian Basin, then combined with nitrogen to form ammonia.
Natural gas reforming and carbon capture:
This process produces Blue Ammonia by reforming natural gas while simultaneously capturing the resulting carbon emissions.
Carbon storage:
Leveraging subsurface expertise, the captured CO2 is permanently stored underground.
Low carbon ammonia production:
The resulting ammonia is a carbon-free fuel that is more energy-dense than hydrogen and requires less storage space.
Storage and transportation:
Ammonia is stored as a liquid in specialized high-pressure or low-temperature tanks, ready for transport to off-takers.
Bunkering (refueling):
Ammonia is transferred from shore to ship via dedicated loading arms. This process requires specialized port infrastructure and strict safety protocols.
Engine combustion:
Specialized ammonia-ready engines burn the fuel directly for power, resulting in zero CO2 emissions at the point of use.
Contact the ExxonMobil Low Carbon Solutions team to explore how we can achieve lower emissions, together.
-
Contact us
Discover how ExxonMobil Low Carbon Solutions can support your decarbonization strategy.Get in touch -
Explore more
Learn more about how we’re delivering real world projects to reduce emissions and unlock value.See our progress -
Follow us
Stay connected with us on LinkedIn for more insights on the energy transition.Follow us on LinkedIn
FOOTNOTES:
- US EPA. (April 25, 2025). Carbon Pollution from Transportation. https://www.epa.gov/transportation-air-pollution-and-climate-change/carbon-pollution-transportation.
- UN Trade & Development. (2022). Roadmap to decarbonize the shipping sector: Technology development, consistent policies and investment in research, development and innovation. https://unctad.org/news/transport-newsletter-article-no-99-fourth-quarter-2022.
- Global Maritime Forum. (2024). The scale of investment needed to decarbonize international shipping. https://globalmaritimeforum.org/insight/the-scale-of-investment-needed-to-decarbonize-international-shipping/.
- ExxonMobil Global Outlook
- Expected smaller footprint of lithium mining and expected lower carbon and water impacts: EM analysis of external sources and third party life-cycle analyses. a) Vulcan Energy, 2022 https://v-er.eu/app/uploads/2023/11/LCA.pdf, Minviro publication. Grant, A., Deak, D., & Pell, R. (2020). b) The CO2 Impact of the 2020s Battery Quality Lithium Hydroxide Supply Chain-Jade Cove Partners. https://www.jadecove.com/research/liohco2impact. Kelly, J. C., Wang, M., Dai, Q., & Winjobi, O. (2021). c) Energy, greenhouse gas, and water life cycle analysis of lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide monohydrate from brine and ore resources and their use in lithium ion battery cathodes and lithium ion batteries. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 174, 105762.






